What Solar Panel Do, Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity through the use of photovoltaic cells. They are an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution for generating clean energy.

Solar panels harness the power of the sun to produce electricity, which can be used for a variety of purposes, such as powering homes, businesses, and even charging electric vehicles. With advancements in technology, solar panels have become more efficient and affordable, making them a popular choice for those looking to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and lower their carbon footprint.
By installing solar panels, individuals and businesses can contribute to a more sustainable future while also saving on their energy costs.
Credit: ecoactions.homedepot.com
Solar panels harness the renewable energy of sunlight to generate electricity cleanly and sustainably. They are a key component of the transition to renewable energy sources and play a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
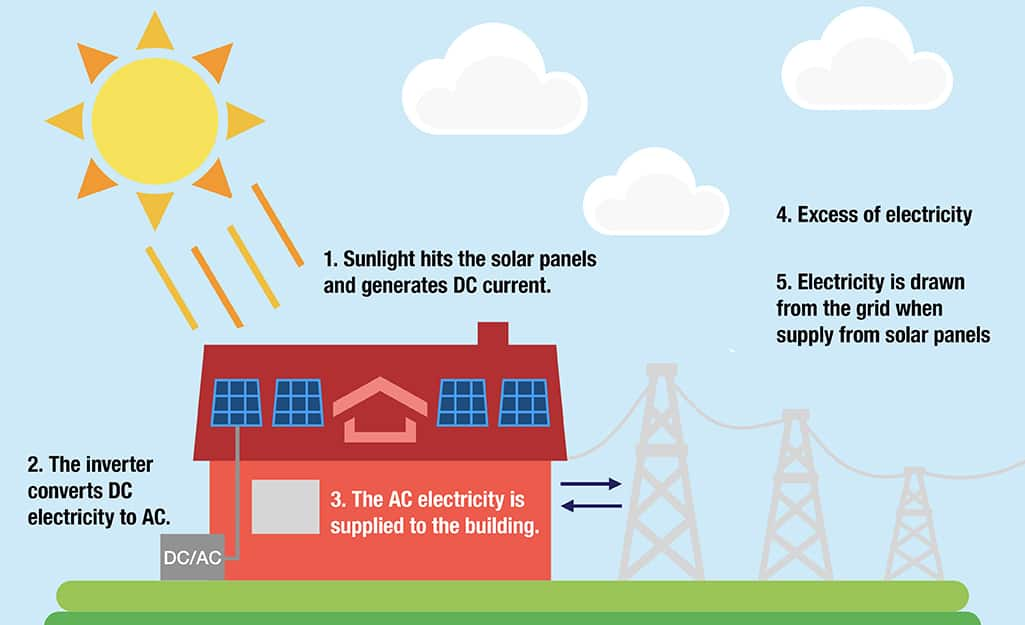
Solar panels work by converting sunlight into electricity through a process known as the photovoltaic effect. Here’s how it works:
-
Solar Cells: Solar panels are made up of individual solar cells, typically composed of semiconductor materials such as silicon. When sunlight strikes the surface of a solar cell, it excites electrons within the material, creating an electric current.
-
Photovoltaic Effect: The photovoltaic effect occurs when photons (particles of light) from the sun are absorbed by the solar cells, causing electrons to be released from their atoms. This creates an electric potential difference, or voltage, between the front and back of the solar cell.
-
Electricity Generation: The electric current generated by the excited electrons flows through the semiconductor material and into metal conductors embedded within the solar panel. These conductors collect the electrical energy and channel it out of the solar panel as direct current (DC) electricity.
-
Inverter Conversion: The DC electricity produced by the solar panels is then fed into an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC) electricity. AC electricity is the type of power used in most homes and businesses.
-
Grid Connection (Optional): The converted AC electricity can be used to power electrical appliances and devices within the home. Excess electricity generated by the solar panels can be fed back into the electrical grid if the system is connected to a grid-tied setup.
-
Off-Grid Systems: In off-grid solar panel systems, the generated electricity is stored in batteries for later use when sunlight is not available, such as during nighttime or cloudy days. This allows off-grid systems to operate independently of the electrical grid.
-
Net Metering (Grid-Tied Systems): In grid-tied solar panel systems with net metering, any excess electricity generated by the solar panels is fed back into the grid, and the system owner receives credit for the surplus electricity. This can offset electricity costs and provide additional financial benefits.
Solar panels are becoming an increasingly popular choice for renewable energy sources due to their environmental benefits and cost-efficient nature. One of the most common questions about solar panels is, “How do solar panels work?” Understanding the underlying mechanisms of solar panels can help individuals make more informed decisions about incorporating this technology into their lives.
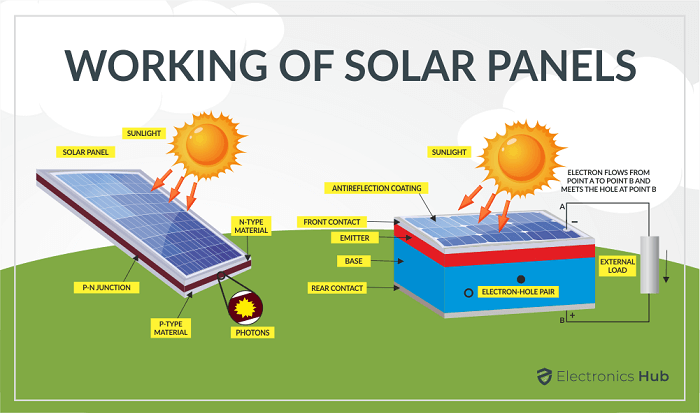
Photovoltaic Effect
The photovoltaic effect is the foundation of how solar panels function. When photons of sunlight hit the surface of a solar panel, they cause electrons in the panel’s semiconductor material to become energized. This energization creates an electric field, resulting in the movement of electrons, generating an electrical current in the process.
Conversion Of Sunlight Into Electricity
After the photovoltaic effect initiates the movement of electrons, the solar panel’s components work together to convert this solar energy into usable electricity. The generated electrical current is directed through the wiring of the solar panel to an inverter, a device that converts this direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to power household appliances and other electrical devices.
Types Of Solar Panels
There are several types of solar panels available, each with its own unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. The main types of solar panels include:
-
Monocrystalline Solar Panels: Monocrystalline solar panels are made from single-crystal silicon, giving them a uniform appearance and higher efficiency compared to other types. They typically have a higher power output and better performance in low-light conditions. Monocrystalline panels are ideal for residential and commercial installations where space is limited and efficiency is prioritized.
-
Polycrystalline Solar Panels: Polycrystalline solar panels are made from multiple silicon crystals, which are melted together to form the panel’s surface. They are less expensive to manufacture than monocrystalline panels but generally have slightly lower efficiency and performance. Polycrystalline panels are suitable for larger-scale installations where cost-effectiveness is a priority.
-
Thin-Film Solar Panels: Thin-film solar panels are made by depositing thin layers of semiconductor material onto a substrate, such as glass or metal. They are lighter, more flexible, and less expensive to produce than crystalline silicon panels. Thin-film panels have lower efficiency but can be integrated into building materials, such as roofing shingles or facades, making them suitable for architectural applications and off-grid installations.
-
Bifacial Solar Panels: Bifacial solar panels can generate electricity from both the front and back sides of the panel, capturing sunlight reflected off surfaces such as the ground or nearby structures. They typically have transparent backsheets or glass on the rear side to allow light to pass through. Bifacial panels offer higher energy yields and can be advantageous in certain environments with reflective surfaces.
-
PERC Solar Panels: Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC) solar panels feature a rear-side passivation layer that improves light absorption and electron capture, leading to higher efficiency and power output. PERC panels are increasingly popular in the solar industry due to their improved performance and cost-effectiveness.
-
Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) Solar Panels: Cadmium telluride solar panels are thin-film panels that use cadmium telluride as the semiconductor material. They offer lower manufacturing costs and competitive efficiency levels, making them attractive for utility-scale solar projects and large installations.
-
Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS) Solar Panels: CIGS solar panels are another type of thin-film technology that uses a combination of copper, indium, gallium, and selenium as the semiconductor material. They offer high efficiency and can be manufactured using a variety of flexible substrates, making them suitable for applications where flexibility and lightweight design are important.
Solar panels are a crucial component of a solar power system, converting sunlight into usable electricity. They come in various types, each with its own characteristics and advantages. Understanding the different types of solar panels can help you make an informed decision about which one is best suited for your energy needs. In this article, we will discuss three major types of solar panels: Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin-Film.
Monocrystalline
Monocrystalline solar panels are widely recognized for their high efficiency and sleek appearance. They are created from a single crystal structure, usually made from silicon. Their uniform black color enhances their aesthetics, making them a popular choice for residential and commercial installations. Due to their higher efficiency, monocrystalline panels require less space compared to other types.
Polycrystalline
Polycrystalline solar panels, also known as multicrystalline panels, are made from multiple fragments of silicon crystals. They have a signature blue hue, resulting from the crystal structure. While polycrystalline panels tend to be less efficient than monocrystalline panels, advancements in technology have narrowed the efficiency gap. They are often more affordable than monocrystalline panels and suitable for large-scale installations where ample space is available.
Thin-film
Thin-film solar panels offer a lightweight and flexible alternative to traditional crystalline panels. They are typically made by depositing thin layers of photovoltaic materials onto a substrate, such as glass, plastic, or metal. Thin-film panels are advantageous in situations where weight and portability are key considerations, such as on rooftops with weight restrictions or curved surfaces. However, their lower efficiency compared to crystalline panels makes them less efficient in generating electricity in smaller spaces.
Factors To Consider When Choosing Solar Panels
When selecting solar panels, several factors need consideration. Efficiency, cost, durability, and warranty are some key aspects to evaluate before making a decision. Additionally, the size and type of solar panel that meets your energy needs and the compatibility with your electrical system are essential factors to ponder.

When choosing solar panels for your home or business, there are several important factors to consider to ensure you select the right system for your needs. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
- Energy Efficiency: Look for solar panels with high energy efficiency ratings, as this will determine how much electricity the panels can generate from sunlight. Higher efficiency panels typically have a higher power output per square meter of space, which can be beneficial if you have limited roof space or want to maximize energy production.
- Cost: Consider the upfront cost of the solar panels and balance it against the long-term savings on your energy bills. While higher efficiency panels may have a higher initial cost, they can also provide greater energy savings over time. Compare the cost per watt of different solar panels to determine the best value for your budget.
- Quality and Durability: Choose solar panels from reputable manufacturers with a proven track record of quality and reliability. Look for panels that are certified by recognized testing organizations, such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) or Underwriters Laboratories (UL). Consider the warranty offered by the manufacturer, including both product warranties and performance warranties.
- Aesthetics: Consider the appearance of the solar panels and how they will look once installed on your property. Some homeowners prefer sleek, black panels that blend in seamlessly with the roof, while others may prefer more traditional blue panels. Choose panels that complement the architectural style of your home and meet any homeowner association (HOA) or local zoning requirements.
- Available Space: Assess the available space on your roof or property to determine how many solar panels you can install. Consider factors such as roof orientation, tilt angle, shading from trees or buildings, and any obstructions that may impact solar panel performance. Choose panels that can be configured to fit your available space and maximize energy production.
- Installation Requirements: Consider the installation requirements of the solar panels, including mounting hardware, wiring, and inverters. Choose panels that are compatible with your existing electrical system and can be installed safely and efficiently by a qualified installer.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the environmental impact of the solar panels, including their manufacturing process, materials used, and end-of-life disposal. Look for panels that are made with sustainable materials and have a low carbon footprint. Choose panels that are certified as environmentally friendly by third-party organizations, such as the Green Energy Certification Scheme (GECS) or the Cradle to Cradle CertifiedTM program.
- Local Incentives and Rebates: Check for any local incentives, rebates, or tax credits available for installing solar panels in your area. These incentives can help offset the upfront cost of the solar panels and provide additional savings over time. Be sure to research the eligibility requirements and application process for any incentives you plan to apply for.
Efficiency
Solar panels play a vital role in harnessing the sun’s energy and converting it into usable electricity. When considering solar panels for your home or business, one of the most important factors to consider is their efficiency. Efficiency refers to the ability of solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity. It is typically measured as a percentage and represents the amount of energy produced by the panel relative to the amount of sunlight it receives.
Cost
Another crucial factor to consider when choosing solar panels is the cost. Solar panels vary in price depending on several factors, including their size, efficiency, and manufacturer. Although investing in solar panels may seem expensive upfront, it is essential to consider the long-term savings they can provide. By generating your own electricity, you can significantly reduce or even eliminate your monthly energy bills, making solar panels a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Durability
Durability is an important consideration when selecting solar panels. Since solar panels are exposed to various weather conditions, including hail, wind, and rain, it is crucial to choose panels that can withstand these elements. Look for solar panels that are made with durable materials and have a high resistance to impact. Additionally, consider the warranty offered by the manufacturer, as it can provide peace of mind regarding the longevity of your investment.
Aesthetics
Aesthetics may be a factor to consider, particularly for residential installations. Solar panels come in different sizes and designs, and selecting panels that complement the appearance of your property is an important consideration for many homeowners. Fortunately, solar technology has advanced significantly, and there are now more options available when it comes to visually appealing solar panels. Whether you prefer all-black panels or those with a sleek design, you can find solar panels that blend seamlessly with your home’s architecture.

Credit: www.goodenergy.co.uk
Installation And Maintenance Of Solar Panels
Installation and Maintenance of Solar Panels
Installing and maintaining solar panels is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your solar energy system. Here’s a guide on installation and maintenance practices:
Installation:
-
Site Assessment: Before installation, conduct a site assessment to evaluate factors such as roof orientation, tilt angle, shading, and available space. Choose the best location for solar panel placement to maximize sunlight exposure and energy production.
-
Permits and Regulations: Obtain any necessary permits and approvals required for solar panel installation from local authorities or homeowner associations. Ensure compliance with building codes, zoning regulations, and other legal requirements.
-
Selecting Equipment: Choose high-quality solar panels, inverters, mounting hardware, and other components from reputable manufacturers. Consider factors such as efficiency, durability, warranty, and compatibility with your electrical system.
-
Mounting: Install mounting racks or frames securely onto the roof or ground surface, following manufacturer guidelines and local building codes. Ensure proper orientation and tilt angle for optimal sunlight exposure.
-
Wiring and Connection: Connect the solar panels, inverters, and other components using appropriate wiring and connectors. Follow electrical safety standards and guidelines to prevent hazards such as electric shocks or fire.
-
Inverter Installation: Install the inverter in a well-ventilated, shaded area, preferably indoors or in a weatherproof enclosure. Ensure proper wiring connections and ventilation to prevent overheating.
-
Grid Connection (if applicable): If your system is grid-tied, coordinate with your utility company to establish connection and metering arrangements. Install a bi-directional meter to measure both energy consumption and excess energy fed back into the grid.
-
Commissioning and Testing: Test the solar energy system to verify proper functionality and performance. Conduct a commissioning process to ensure all components are operating correctly and safely.
Maintenance:
-
Regular Cleaning: Keep solar panels clean and free of dirt, dust, debris, and bird droppings to maximize sunlight absorption. Clean panels with water and a soft brush or sponge regularly, especially in dusty or polluted areas.
-
Inspecting for Damage: Periodically inspect the solar panels, mounting hardware, wiring, and other components for signs of damage, corrosion, wear, or deterioration. Look for cracks, loose connections, or physical damage that may affect performance.
-
Monitoring Performance: Monitor the performance of your solar energy system regularly using monitoring software or online platforms provided by the manufacturer or installer. Track energy production, system efficiency, and any deviations from expected performance.
-
Trimming Vegetation: Trim trees, branches, or foliage that may cast shadows on solar panels and reduce energy production. Maintain clear airspace around panels to maximize sunlight exposure throughout the day.
-
Inverter Maintenance: Check the inverter regularly for proper operation, error codes, or warning indicators. Clean the ventilation openings and ensure adequate airflow to prevent overheating.
-
Battery Maintenance (if applicable): If your system includes battery storage, follow manufacturer recommendations for battery maintenance, such as checking electrolyte levels, cleaning terminals, and performing capacity tests.
-
Professional Inspection: Schedule periodic inspections and maintenance checks by a qualified solar energy technician or installer. Professional inspections can identify potential issues early and ensure proper system operation.
-
Winter Preparations: In colder climates, take precautions to protect solar panels from snow buildup or ice formation. Install snow guards or brush snow off panels to prevent shading and ensure continued energy production.
Solar panels are a sustainable and efficient way to harness the power of the sun and generate clean energy for homes and businesses. In order to ensure the optimal performance of solar panels, proper installation and ongoing maintenance are crucial. This article will delve into the key aspects of installing and maintaining solar panels, covering site evaluation, mounting and wiring, as well as cleaning and inspection.
Site Evaluation
Before the installation of solar panels, a comprehensive site evaluation is essential. This entails assessing the available roof space, orientation, and shading to determine the best location for placement. Factors such as the angle of the roof and the presence of any obstructions can significantly impact the efficiency of solar panel installation. It is vital to ensure that the chosen site receives ample sunlight throughout the day for optimal energy production.
Mounting And Wiring
Once the site evaluation is complete, the next step involves the mounting and wiring of the solar panels. The mounting system must be secure and able to withstand various weather conditions. Additionally, the wiring must be expertly installed to optimize energy generation and ensure the safe and efficient transfer of electricity to the property’s electrical system. Proper grounding and connection to inverters are also key considerations during this phase of the installation process.
Cleaning And Inspection
After the installation, regular cleaning and inspection are crucial for maintaining the efficiency of solar panels. Over time, dirt, dust, and debris can accumulate on the surface, potentially reducing the panels’ ability to capture sunlight. Regular cleaning, using appropriate equipment and techniques, is essential to ensure maximum energy production. Furthermore, periodic inspections are essential to detect any potential issues or damage to the panels, such as cracks or loose connections, which could affect their performance.
Benefits Of Solar Panels
Solar panels offer numerous benefits, making them a popular choice for homeowners, businesses, and communities looking to harness clean, renewable energy. Here are some of the key benefits of solar panels:
-
Clean and Renewable Energy: Solar panels generate electricity using sunlight, a virtually limitless and renewable energy source. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy production does not produce harmful emissions or contribute to air pollution, making it environmentally friendly and sustainable.
-
Reduced Electricity Bills: By generating electricity from sunlight, solar panels can significantly reduce or even eliminate electricity bills for homeowners and businesses. Solar energy systems allow users to produce their electricity, reducing dependence on grid-supplied power and mitigating the impact of rising utility rates.
-
Financial Savings: Investing in solar panels can provide significant financial returns over time. With lower electricity bills and potential incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and net metering programs, homeowners and businesses can recoup their initial investment and enjoy long-term savings on energy costs.
-
Energy Independence: Solar panels enable homeowners and businesses to generate their electricity on-site, reducing reliance on external energy sources and enhancing energy independence. This independence can provide greater stability and resilience against power outages, energy price fluctuations, and supply disruptions.
-
Environmental Benefits: Solar energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change by displacing fossil fuel-based electricity generation. By harnessing clean, renewable energy from the sun, solar panels contribute to environmental conservation, resource preservation, and a cleaner, healthier planet for future generations.
-
Low Maintenance Requirements: Solar panels have minimal maintenance requirements and can operate reliably for 25 years or more with proper care. Routine maintenance, such as cleaning the panels and inspecting for damage, is typically straightforward and can be performed by homeowners or professional installers.
-
Increase Property Value: Homes and businesses equipped with solar panels often command higher property values and sell faster than those without solar installations. Solar panels are considered an attractive feature for prospective buyers, offering long-term energy savings and environmental benefits.
-
Job Creation and Economic Growth: The solar industry is a significant driver of job creation and economic growth, providing employment opportunities in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and related sectors. The growth of the solar industry contributes to local economies, stimulates investment, and fosters innovation in renewable energy technologies.
-
Scalability and Adaptability: Solar energy systems can be customized to meet the specific needs and requirements of different applications, from residential rooftops to large-scale solar farms. Solar panels are scalable and adaptable, allowing for flexible deployment in various environments and geographical locations.
Switching to solar energy can provide numerous benefits for homeowners and businesses alike. Solar panels harness the power of the sun to generate electricity, offering a sustainable and renewable energy solution. Here are the major advantages that come with installing solar panels:
Energy Cost Savings
Solar panels can significantly decrease your energy bills while reducing your reliance on traditional power sources. You can enjoy substantial cost savings on your monthly energy expenses since the sun’s energy is free. With solar panels, you can generate your own electricity and decrease your dependence on utility companies.
Solar energy can be especially advantageous for businesses, as it reduces operational costs and allows for long-term savings. By investing in solar panel installations, businesses can lock in low energy costs for the entire lifespan of the system, which can span several decades.
Environmental Impact
Solar panels have a positive environmental impact due to their ability to harness clean and renewable energy. By using solar power, you can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change. Solar energy systems do not produce harmful byproducts or contribute to air pollution, making them a sustainable choice for the environment.
Additionally, solar energy helps conserve natural resources. By utilizing the sun’s energy, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, coal, and natural gas, which are finite resources that harm the environment during extraction and burning.
Energy Independence
Solar panels offer energy independence by allowing individuals and businesses to generate their own electricity. By investing in a solar energy system, you can reduce your dependence on the power grid and potential fluctuations in energy prices.
This independence provides peace of mind during power outages or natural disasters when the grid may fail. With solar energy, you have a reliable source of power that can keep your essential devices and appliances running.
Furthermore, solar energy promotes energy security. By diversifying our energy sources and reducing reliance on imported fuel, we enhance our nation’s energy independence and reduce vulnerability to geopolitical factors that affect energy prices.
Switching to solar panels not only offers energy cost savings and environmental benefits but also provides energy independence for a more sustainable future.
Challenges And Limitations Of Solar Panels
While solar panels offer numerous benefits, they also face several challenges and limitations that can impact their widespread adoption and effectiveness. Here are some of the key challenges and limitations associated with solar panels:
-
Intermittent Energy Source: Solar energy is intermittent and dependent on sunlight, which varies throughout the day and is affected by factors such as weather, cloud cover, and seasonal changes. This intermittency can lead to fluctuations in energy production and reliability, requiring backup energy storage or grid connection for continuous power supply.
-
Energy Storage Requirements: Solar panels generate electricity only when the sun is shining, necessitating the use of energy storage systems, such as batteries, to store surplus energy for use during periods of low sunlight or at night. Energy storage technologies add complexity and cost to solar energy systems, impacting overall affordability and scalability.
-
High Initial Costs: The upfront cost of purchasing and installing solar panels can be significant, deterring some homeowners, businesses, and communities from adopting solar energy. While solar panel prices have declined in recent years, the initial investment remains a barrier for many individuals and organizations, especially in regions with limited financial incentives or financing options.
-
Space Requirements: Solar panels require adequate space for installation, typically on rooftops or open land areas with unobstructed sunlight exposure. Limited space availability, shading from nearby buildings or trees, and zoning regulations can restrict the feasibility of solar panel installations, particularly in densely populated urban areas or areas with land use restrictions.
-
Resource Intensity and Environmental Impact: The manufacturing and disposal of solar panels involve resource-intensive processes and materials, including silicon, metals, and chemicals, which can have environmental impacts such as resource depletion, water consumption, and waste generation. Additionally, end-of-life management and recycling of solar panels present challenges due to the complex composition and variability of panel designs.
-
Efficiency and Performance Variability: Solar panel efficiency can vary depending on factors such as panel technology, quality, age, and environmental conditions. Lower efficiency panels may require larger installations to achieve desired energy production levels, increasing overall costs and space requirements. Performance degradation over time due to factors such as soiling, shading, and panel aging can also affect long-term energy output.
-
Grid Integration and Regulatory Challenges: Integrating solar energy into existing electrical grids can pose technical and regulatory challenges related to grid stability, voltage management, and power quality. Grid interconnection standards, net metering policies, and utility regulations may vary by region and affect the economic viability and feasibility of solar panel installations.
-
Geographical Limitations: Solar energy availability varies geographically based on factors such as latitude, climate, and sun exposure. Regions with low sunlight intensity or frequent cloud cover may have reduced solar energy potential, limiting the effectiveness of solar panels as a primary energy source.
Solar panels are a popular and environmentally friendly source of energy, but they do come with their fair share of challenges and limitations. It’s important to be aware of these factors before deciding to invest in solar panels for your home or business. In this article, we will discuss three key challenges and limitations of solar panels: intermittent power generation, initial investment, and space requirement.
Intermittent Power Generation
One of the main challenges of solar panels is their intermittent power generation. Solar panels produce electricity only when exposed to sunlight. This means that during cloudy days, at night, or in shaded areas, the amount of electricity generated from solar panels is significantly reduced. Therefore, it’s essential to have a backup energy source or a battery storage system to ensure a continuous power supply.
Initial Investment
The initial investment required to install solar panels can be a significant hurdle for some people. While the long-term savings on electricity bills make solar panels a worthwhile investment, the upfront costs can be substantial. This includes the cost of purchasing the panels, installation, and any additional equipment or permits needed. However, it’s important to note that the prices of solar panels have been decreasing in recent years, making them more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
Space Requirement
Solar panels require a considerable amount of space for installation. The number of panels needed for adequate electricity generation depends on factors such as energy consumption and the efficiency of the panels. For residential installations, roofs are often the preferred location for solar panels. However, if the roof has limited space or is not suitable for installation, alternative solutions such as ground-mount or carport systems may need to be considered. It’s crucial to evaluate the available space and determine if it can accommodate the required number of panels for optimal energy production.
Future Of Solar Panels
The future of solar panels holds promising developments driven by ongoing technological advancements, policy support, and growing market demand for clean, renewable energy solutions. Here are some key trends and potential innovations shaping the future of solar panels:
-
Increased Efficiency: Researchers are continually working to improve the efficiency of solar panels, increasing their ability to convert sunlight into electricity. Advancements in materials science, such as perovskite and tandem solar cells, hold the potential to significantly enhance solar panel efficiency beyond the current limits of silicon-based technology.
-
Tandem Solar Cells: Tandem solar cells combine multiple layers of different materials with complementary absorption spectra to capture a broader range of sunlight wavelengths and increase overall efficiency. Research into tandem solar cell configurations, including perovskite-silicon and perovskite-CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide), could lead to commercially viable tandem solar panels with higher efficiency and lower production costs.
-
Bifacial Solar Panels: Bifacial solar panels, which can capture sunlight from both the front and rear surfaces, offer increased energy generation potential compared to traditional monofacial panels. As manufacturing costs decrease and efficiency improves, bifacial solar panels are expected to gain traction in the market, especially for ground-mounted installations and commercial rooftops.
-
Flexible and Lightweight Designs: Flexible and lightweight solar panels, made possible by thin-film and organic photovoltaic (OPV) technologies, offer greater design flexibility and versatility for integration into various applications, such as building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), portable electronics, and wearable devices. Continued research and development in flexible solar panel materials and manufacturing processes could unlock new opportunities for solar energy deployment.
-
Energy Storage Integration: The integration of energy storage systems, such as lithium-ion batteries and flow batteries, with solar panels enables reliable electricity generation and storage for use during periods of low sunlight or grid outages. Advances in battery technology, including higher energy density, longer cycle life, and lower costs, will enhance the viability and effectiveness of solar-plus-storage solutions for residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications.
-
Smart Grid Integration: Smart grid technologies, such as advanced inverters, grid-interactive inverters, and demand response systems, enable seamless integration of solar energy into existing electrical grids. Smart grid functionalities, such as real-time monitoring, dynamic grid balancing, and demand-side management, optimize energy distribution, improve grid stability, and maximize the value of solar energy resources.
-
Internet of Things (IoT) Connectivity: IoT-enabled solar panel monitoring and control systems provide real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, and remote management capabilities for optimizing solar energy system performance. IoT sensors, communication networks, and cloud-based platforms facilitate proactive maintenance, fault detection, and performance optimization, enhancing the reliability and efficiency of solar panel installations.
-
Circular Economy and Sustainable Manufacturing: The shift towards a circular economy model promotes sustainable practices in solar panel manufacturing, including resource recovery, recycling, and eco-design principles. Closed-loop recycling processes for end-of-life solar panels, coupled with the use of recycled materials and eco-friendly manufacturing techniques, minimize environmental impact and reduce waste generation throughout the solar panel lifecycle.
The Future of Solar Panels looks promising with the continuous advancements in technology. From improved efficiency to integration with energy storage, solar panels are carving the way for sustainable and renewable energy.
Technological Advancements
Solar panels have witnessed significant technological advancements, enhancing their performance and effectiveness. Advancements such as thin-film solar cells and smart solar panel technologies are increasing energy capture and generation from sunlight. These developments are crucial in maximizing the output and minimizing space requirements for solar installations.
Integration With Energy Storage
The integration of solar panels with energy storage technologies such as battery systems is revolutionizing the solar energy sector. This integration allows for power storage during periods of low sun exposure, enabling a consistent and reliable energy supply even when the sun isn’t shining. With this advancement, solar panels are becoming increasingly efficient and reliable as a sustainable energy source.
Credit: www.electronicshub.org
Frequently Asked Questions For What Solar Panel Do
Faq 1: How Do Solar Panels Generate Electricity?
Solar panels generate electricity by converting sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
Faq 2: What Are The Benefits Of Using Solar Panels?
Using solar panels allows you to save on electricity bills, reduce carbon footprint, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Faq 3: Can Solar Panels Work During Cloudy Days?
Yes, solar panels can still generate electricity during cloudy days, although at a lower efficiency compared to sunny days.
Conclusion
In light of the various solar panel options available, it’s crucial to choose the best one for your energy needs. By considering factors such as efficiency, cost, and quality, you can make an informed decision. Take time to research and consult experts to ensure you select the right solar panel for your specific requirements.