To use a solar panel directly without a battery, connect the solar panel directly to the device or appliance you want to power. Instead of storing excess energy in a battery, the solar panel will generate electricity and provide it to the device in real time.

Harnessing solar power directly without the need for intermediate battery storage offers a streamlined and efficient approach to renewable energy utilization. By tapping directly into the sun’s energy, solar panels can generate electricity for immediate use, powering homes, businesses, and communities with clean and sustainable energy. In this guide, we explore the concept of using solar panels directly without batteries, discussing the benefits, applications, and considerations involved. From grid-tied systems to solar water pumping and off-grid applications, direct solar energy usage presents an array of opportunities for reducing reliance on fossil fuels, lowering energy costs, and contributing to environmental sustainability. Join us as we delve into the world of direct solar energy utilization, uncovering its potential to transform the way we power our lives while minimizing our carbon footprint.
By eliminating the need for a battery, you can save on cost and maintenance. Whether you are camping or want to power simple devices like lights or fans, using a solar panel directly can be a convenient and efficient solution.

Credit: www.youtube.com Solar Panel Directly Without Battery
Understanding Direct Solar Energy Usage
Understanding direct solar energy usage involves harnessing solar radiation directly for various applications without the need for intermediate conversion processes. Here’s an overview:
- Solar Thermal Applications:
- Solar thermal technologies capture solar radiation to directly heat water, air, or other fluids for heating purposes. This can include solar water heaters for domestic hot water production, solar space heating systems for buildings, and solar air heaters for ventilation and drying applications. In these systems, solar collectors absorb sunlight and transfer the heat to a fluid, which is then circulated to provide space heating or hot water.
- Solar Cooking and Food Processing:
- Solar cookers and ovens utilize concentrated sunlight to cook food without the need for traditional fuels such as gas or electricity. These devices typically consist of reflective surfaces or concentrators that focus sunlight onto a cooking vessel, effectively harnessing solar energy for cooking, baking, and food processing. Solar cooking is particularly suitable for off-grid or rural areas where access to fuel sources is limited.
- Solar Desalination and Distillation:
- Solar desalination and distillation systems use solar energy to evaporate and condense water, producing freshwater from saltwater or contaminated sources. These systems can provide clean drinking water in arid regions or coastal areas where freshwater resources are scarce. Solar stills and solar desalination plants utilize solar collectors or greenhouse structures to heat water and facilitate the purification process.
- Solar Water Pumping:
- Solar-powered water pumping systems use photovoltaic (PV) panels to directly power water pumps for irrigation, livestock watering, and off-grid water supply applications. These systems eliminate the need for diesel generators or grid electricity, providing a sustainable and cost-effective solution for water management in remote or rural areas. Solar water pumping can help improve agricultural productivity and access to clean water in developing regions.
- Solar Ventilation and Cooling:
- Solar ventilation and cooling systems harness solar energy to power fans or ventilation systems for air circulation and cooling in buildings. Solar attic fans, solar-powered exhaust fans, and passive solar cooling techniques utilize sunlight to reduce indoor temperatures, improve indoor air quality, and enhance comfort without relying on grid electricity or conventional air conditioning.
- Solar Lighting and Daylighting:
- Solar lighting systems utilize solar energy to power LED lights for indoor and outdoor illumination. Solar-powered streetlights, garden lights, and portable solar lanterns harness sunlight during the day and store energy in batteries for nighttime lighting. Daylighting systems incorporate skylights, light tubes, and reflective surfaces to optimize natural sunlight in buildings, reducing the need for artificial lighting and energy consumption.
- Solar-powered Gadgets and Electronics:
- Various portable gadgets and electronics, such as solar chargers, solar backpacks, and solar-powered phone chargers, directly utilize solar energy to recharge batteries and power electronic devices. These devices incorporate small photovoltaic panels to convert sunlight into electricity, providing convenient and eco-friendly charging solutions for on-the-go use.
Understanding direct solar energy usage is crucial in unlocking the full potential of solar power as a renewable energy source. By bypassing the need for battery storage, direct solar energy usage allows for immediate utilization of the electricity generated by solar panels. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of direct solar energy usage, exploring its benefits, applications, and considerations. From grid-tied systems to off-grid setups, understanding how to harness solar energy directly opens up opportunities for sustainable power generation in diverse settings. Join us as we unravel the principles and practicalities of direct solar energy usage, empowering individuals and communities to embrace clean, renewable energy solutions for a brighter and more sustainable future.
How Direct Solar Energy Usage Works
Solar panel systems can be used directly without batteries by connecting the solar panels directly to the electrical load. When sunlight hits the solar panels, they produce direct current (DC) electricity. This electricity can be used to power various devices and appliances immediately without the need for energy storage in batteries. Solar panel systems can indeed be used directly without the need for batteries, offering a streamlined and efficient approach to harnessing solar energy. Unlike systems with battery storage, which store excess energy for later use, direct solar panel systems immediately convert sunlight into usable electricity without an intermediate storage step. This direct utilization of solar power is particularly advantageous for certain applications where continuous energy generation or real-time consumption is desired, such as grid-tied systems, solar water pumping, daytime operation of appliances, and solar lighting. By eliminating the need for batteries, direct solar panel systems can simplify system design, reduce costs, and maximize energy efficiency, making them a practical and versatile solution for various residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
- Cost-effective: By eliminating the need for batteries, direct solar energy usage can save on the cost of purchasing and maintaining battery storage systems.
- Efficiency: The direct use of solar energy leads to reduced energy losses and higher overall system efficiency.
- Simple setup: Using solar panels directly without batteries simplifies the system setup and reduces maintenance requirements.
Credit: www.tanfon.com
Components Required For Direct Solar Energy Usage
Embarking on the journey of direct solar energy usage involves understanding and assembling key components that enable the immediate conversion of sunlight into electricity without the need for energy storage. In this exploration, we’ll navigate through the essential elements required for direct solar energy utilization.
From solar panels, the stalwarts capturing sunlight, to inverters that transform direct current into usable alternating current, each component plays a crucial role in this streamlined approach to renewable energy. Join us as we unravel the components that form the backbone of direct solar energy usage, offering insights into the technology that powers a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
Direct solar energy usage refers to the utilization of solar power without the need for intermediate storage in batteries. Here are the main components required for setting up a direct solar energy usage system:
-
Solar Panels:
- Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) modules, are the primary components responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. These panels consist of multiple solar cells made of semiconductor materials that generate DC (direct current) electricity when exposed to sunlight.
-
Inverter:
- An inverter is essential for converting the DC electricity produced by the solar panels into AC (alternating current) electricity, which is compatible with most household appliances and electrical loads. Inverters come in various types, including string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers.
-
Mounting Structure:
- Mounting structures or racks are used to securely install and support the solar panels in the desired location, such as rooftops, ground mounts, or pole mounts. These structures are typically made of aluminum or galvanized steel and are designed to withstand various weather conditions.
-
Wiring and Electrical Components:
- Wiring, cables, connectors, and electrical components are necessary for connecting the solar panels to the inverter and electrical loads. DC wiring connects the solar panels to the inverter, while AC wiring connects the inverter to the main electrical panel or distribution system.
-
Disconnect Switches:
- Disconnect switches or circuit breakers are installed between the solar panels, inverters, and electrical loads to isolate the system from the grid or other power sources during maintenance or emergencies. These switches ensure safe operation and compliance with electrical codes.
-
Monitoring System:
- A monitoring system allows users to track the performance and output of the solar panel system in real-time. Monitoring systems may include software, meters, or online platforms that display energy production data, system status, and alerts for any issues or abnormalities.
-
Load Appliances and Devices:
- Electrical loads, such as appliances, lighting, electronics, and machinery, are connected directly to the AC output of the inverter to utilize the electricity generated by the solar panels. These loads consume the solar energy produced in real-time without the need for battery storage.
-
Optional: Charge Controller (For Off-Grid Systems):
- In off-grid solar panel systems where batteries are not used, a charge controller may be installed to regulate the voltage and current from the solar panels to prevent overcharging of connected loads or devices.
When it comes to harnessing solar energy directly without the need for batteries, there are a few essential components that you will need. These components include a solar panel, charge controller, inverter, and load. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the efficient utilization of solar power. Let’s take a closer look at these components and their functions:
Solar Panel
A solar panel is the heart of any solar power system. It converts sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Solar panels are made up of multiple solar cells that capture sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity. The size and capacity of the solar panel depend on your energy requirements. It is crucial to place the solar panel in an area where it can receive maximum sunlight for optimal energy production.
Charge Controller
A charge controller is a device that regulates the amount of current flowing from the solar panel to the battery. However, in a direct solar energy usage setup, the charge controller serves a different purpose. It ensures that the electricity generated by the solar panel is directly supplied to the load without overcharging it. The charge controller safeguards against any potential electrical damage and prevents excessive power loss, enhancing the overall efficiency of the system.
Inverter
An inverter is responsible for converting the DC electricity produced by the solar panel into alternating current (AC) electricity suitable for powering household appliances. In a direct solar energy usage configuration, the inverter converts the DC electricity directly into AC electricity to power the load without the need for batteries. It is important to choose an inverter that matches the power requirements of your load to ensure smooth and uninterrupted electricity supply.
Load
The load refers to the electrical appliances or devices that you want to power using the solar energy generated. These can include lights, fans, refrigerators, or any other household appliances that operate on AC electricity. It is advisable to calculate the power consumption of your load to determine the appropriate size and capacity of your solar panel and inverter. Additionally, energy-efficient appliances and LED lights can further optimize the utilization of solar power.
By having these key components – solar panel, charge controller, inverter, and load – you can make the most of solar energy without the need for batteries. In the next section, we will delve deeper into each component’s functionality and their interplay within the system.
When it comes to harnessing solar energy, traditional methods often involve storing excess power in batteries for later use. However, there’s an alternative approach that bypasses this step entirely: direct utilization of solar energy to power loads in real-time. In this setup, solar panel systems generate electricity from sunlight and feed it directly into electrical loads without the need for energy storage.
This method offers immediate access to clean, renewable energy, making it an attractive option for applications where continuous power supply is essential. Whether for powering appliances, lighting, or other electrical devices, direct utilization of solar panel systems provides a streamlined and efficient way to meet energy needs while reducing reliance on grid electricity and minimizing costs. In this exploration, we’ll delve into the advantages, considerations, and practical applications of using solar panel systems directly to power various loads, offering insights into its feasibility and benefits in different contexts.
Steps To Set Up Direct Solar Energy Usage
Discover the steps to set up direct solar energy usage without a battery, allowing you to harness the power of solar panels directly.
Setting up direct solar energy usage involves several steps to ensure the efficient and effective utilization of solar power without the need for batteries. Here’s a guide to the process:
- Assess Energy Needs:
- Determine the energy requirements of the loads you intend to power directly with solar energy. Identify the types of electrical devices, appliances, or equipment that will be connected to the solar panel system.
- Calculate Solar Panel Capacity:
- Calculate the total power consumption (in watts) of the connected loads to determine the required capacity of the solar panel system. Ensure that the solar panel capacity meets or exceeds the total power demand of the loads.
- Select Solar Panels:
- Choose high-quality solar panels with appropriate capacity, efficiency, and durability for your application. Consider factors such as available sunlight, panel size, mounting options, and budget constraints.
- Determine Inverter Requirements:
- Select an inverter or power converter suitable for converting the DC (direct current) output from the solar panels into AC (alternating current) electricity compatible with your loads. Ensure that the inverter’s capacity matches the maximum power output of the solar panels.
- Design Electrical Wiring:
- Plan the electrical wiring layout to connect the solar panels to the inverter and the loads. Use appropriate cables, connectors, and circuit protection devices to ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Install Solar Panels:
- Mount the solar panels in a location with optimal sunlight exposure, such as rooftops, ground mounts, or pole mounts. Follow manufacturer’s instructions and local building codes for proper installation and secure mounting.
- Connect Solar Panels to Inverter:
- Wire the solar panels in parallel or series configuration, depending on the system voltage and inverter specifications. Connect the DC output cables from the solar panels to the input terminals of the inverter.
- Connect Loads to Inverter:
- Connect the electrical loads directly to the AC output terminals of the inverter using appropriate wiring and connectors. Ensure that the inverter is properly sized to handle the maximum power demand of the connected loads.
- Test and Commission System:
- Test the functionality of the solar panel system by verifying proper wiring connections, voltage levels, and load operation. Commission the system to ensure that it is operating safely and efficiently.
- Monitor and Maintain System:
- Regularly monitor the performance of the solar panel system to ensure optimal energy production and load operation. Clean the solar panels periodically to remove dirt, debris, and shading that may reduce efficiency.
By bypassing battery storage, this approach allows for immediate utilization of solar power. In this guide, we’ll navigate through the steps required to establish direct solar energy usage. From selecting the right solar panels to configuring inverters and connecting electrical loads, each step is crucial in creating a seamless and efficient system. Join us as we delve into the process of setting up direct solar energy usage, empowering individuals and communities to embrace sustainable energy solutions for a brighter and greener future.
When it comes to harnessing solar energy, using solar panels directly without batteries can be an efficient and cost-effective solution. By eliminating the need for batteries, you can increase the overall efficiency of your solar energy system. In this article, we will guide you through the steps to set up direct solar energy usage. So let’s get started!
Choosing The Right Solar Panel
The first step in setting up direct solar energy usage is to choose the right solar panel for your needs. Consider factors such as the wattage and voltage output of the panel. It’s important to select a solar panel that matches the energy requirements of your load. Additionally, make sure to check the efficiency rating of the panel to ensure maximum power output.
Selecting A Suitable Charge Controller
Once you have chosen the right solar panel, the next step is to select a suitable charge controller. The charge controller acts as a regulator between the solar panel and the load. It prevents overcharging of the load and protects it from voltage spikes. When selecting a charge controller, consider aspects such as its capacity, type (PWM or MPPT), and compatibility with your solar panel and load.
Connecting The Solar Panel To The Charge Controller
After selecting the charge controller, it’s time to connect the solar panel to the charge controller. Begin by ensuring that the solar panel’s positive (+) and negative (-) terminals are correctly identified. Connect the positive terminal of the solar panel to the positive terminal of the charge controller and the negative terminal to the negative terminal of the charge controller. This establishes the connection between the solar panel and the charge controller.
Connecting The Charge Controller To The Inverter
Next, connect the charge controller to the inverter. The inverter converts the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panel into alternating current (AC) suitable for powering your load. Ensure that the positive terminal of the charge controller is connected to the positive terminal of the inverter, and the negative terminal of the charge controller is connected to the negative terminal of the inverter. This establishes the connection between the charge controller and the inverter.
Connecting The Inverter To The Load
Finally, connect the inverter to the load that you want to power with solar energy. Identify the positive and negative terminals of the load and connect them to the respective terminals of the inverter. Once the connections are made, the solar panel will directly power the load through the charge controller and the inverter, providing you with direct solar energy usage.
In conclusion, setting up direct solar energy usage without batteries requires careful consideration of the solar panel, charge controller, inverter, and load. By following these steps, you can efficiently harness solar energy and reduce your reliance on traditional power sources. So go ahead, make the most of the sun’s energy and embrace a sustainable future!
Maintenance And Troubleshooting Tips
Learn how to efficiently use solar panels without the need for batteries with these maintenance and troubleshooting tips. Harness the power of the sun directly, ensuring optimal performance and sustainable energy.
Maintaining and troubleshooting a direct solar energy usage system is essential for ensuring optimal performance and reliability over time. From regular upkeep to identifying and resolving issues, proactive measures can help maximize energy output and minimize downtime. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore maintenance and troubleshooting tips tailored to direct solar energy usage systems. Whether you’re a homeowner, business owner, or solar professional, understanding these strategies is key to ensuring the long-term success of your solar investment. Join us as we navigate through best practices and expert advice to keep your direct solar energy usage system operating at its best.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Maintaining a direct solar energy usage system and troubleshooting any issues that arise are essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here are some maintenance and troubleshooting tips to help keep your system running smoothly:
Maintenance Tips:
-
Regular Cleaning: Keep the solar panels clean and free of dirt, dust, pollen, leaves, and other debris that can reduce sunlight absorption and decrease energy production. Clean the panels periodically with water and a soft brush or sponge, avoiding abrasive materials that could scratch the surface.
-
Inspect Wiring and Connections: Check the electrical wiring, connectors, and junction boxes for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Tighten any loose connections and replace damaged components as needed to ensure proper electrical conductivity and safety.
-
Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor the performance of the solar panel system, including energy production, voltage levels, and load operation. Use monitoring tools or software to track energy generation and identify any fluctuations or abnormalities that may indicate system issues.
-
Trim Vegetation: Trim or remove any vegetation, trees, branches, or structures that may cast shadows or obstruct sunlight from reaching the solar panels. Maintain clear access to sunlight throughout the day to maximize energy production.
-
Inspect Mounting Hardware: Check the mounting hardware, brackets, rails, and fasteners securing the solar panels for stability and integrity. Tighten any loose bolts or screws and replace damaged hardware to prevent panel movement or detachment.
-
Check Inverter Operation: Monitor the operation of the inverter or power converter to ensure it is functioning properly and efficiently. Check for error codes, warning lights, or unusual noises that may indicate inverter malfunctions or performance issues.
Troubleshooting Tips:
-
Check Power Output: If the system is not producing the expected amount of power, verify that the solar panels are receiving adequate sunlight and that there are no obstructions or shading affecting panel performance. Measure the voltage and current output of the solar panels to identify any issues with energy production.
-
Inspect Inverter: If the electrical loads are not receiving power or the inverter is displaying error codes, inspect the inverter for faults or malfunctions. Check the input voltage, output voltage, and status indicators to diagnose potential issues with the inverter.
-
Test Electrical Connections: Verify the integrity of the electrical connections, cables, and terminals between the solar panels, inverter, and loads. Use a multimeter to test for continuity, voltage levels, and resistance to identify any wiring faults or loose connections.
-
Review System Configuration: Ensure that the solar panel system is configured correctly, including the wiring layout, panel orientation, and inverter settings. Consult the system documentation or manufacturer’s guidelines to troubleshoot configuration issues and optimize system performance.
-
Consult Manufacturer Support: If troubleshooting efforts are unsuccessful or if you encounter complex technical issues, contact the manufacturer or a certified solar installer for assistance. Manufacturer support teams can provide troubleshooting guidance, warranty assistance, and technical expertise to resolve system issues effectively.
When using solar panels directly without a battery, it’s essential to stay on top of maintenance and be prepared to troubleshoot any issues that may arise. By following these maintenance and troubleshooting tips, you can ensure that your solar panels continue to operate efficiently and effectively.
Regular Cleaning Of Solar Panels
To maintain optimal performance, it’s crucial to regularly clean your solar panels. Over time, dust, dirt, and other debris can accumulate on the panels, reducing their ability to generate electricity. Use a soft brush or cloth and gentle detergent to remove any buildup, ensuring that the panels are free from obstruction. Plan for regular cleaning to prevent any loss in efficiency.
Regular cleaning of solar panels is essential for maintaining optimal performance and maximizing energy production. Here’s how to clean your solar panels effectively:
-
Safety Precautions:
- Before cleaning your solar panels, ensure your safety by turning off the system and following any specific safety guidelines provided by the manufacturer. Additionally, use appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety goggles, especially when working on rooftops.
-
Check Manufacturer’s Recommendations:
- Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for cleaning and maintenance. Some manufacturers may provide specific instructions or restrictions regarding cleaning agents, tools, and techniques to avoid damaging the panels.
-
Choose the Right Time:
- Clean your solar panels during cooler times of the day, such as early morning or late afternoon, to avoid rapid drying of cleaning solutions, which can leave residue or streaks on the panels.
-
Gather Cleaning Supplies:
- Prepare the necessary cleaning supplies, including a bucket of warm water, mild detergent or soap (non-abrasive and non-ammonia-based), a soft brush or sponge, and a squeegee or soft cloth for drying.
-
Remove Debris:
- Start by gently removing any loose debris, such as dust, leaves, bird droppings, or pollen, from the surface of the solar panels using a soft brush or leaf blower. Avoid using abrasive materials or high-pressure water, as they can scratch or damage the panels.
-
Clean with Soapy Water:
- Mix a small amount of mild detergent or soap with warm water in a bucket to create a cleaning solution. Dip the soft brush or sponge into the soapy water and gently scrub the surface of the solar panels in a circular motion to remove dirt, grime, and stubborn stains.
-
Rinse Thoroughly:
- After scrubbing, rinse the solar panels thoroughly with clean water to remove any soap residue or remaining dirt. Use a hose or gentle spray nozzle to rinse the panels, ensuring that all cleaning solution is washed away.
-
Dry with Soft Cloth or Squeegee:
- Use a squeegee or soft cloth to dry the surface of the solar panels and remove excess water. Wipe gently in a horizontal or vertical motion to avoid streaking, and ensure that the panels are completely dry before reactivating the system.
-
Inspect for Damage:
- While cleaning, inspect the solar panels for any signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or hotspots. If you notice any damage, contact a professional solar installer for further assessment and repair.
-
Schedule Regular Cleaning:
- Establish a regular cleaning schedule based on your location, climate, and environmental conditions. In areas with heavy dust, pollen, or bird activity, more frequent cleaning may be necessary to maintain optimal performance.
Checking And Replacing Faulty Components
Periodically check the components of your solar panel system for any signs of damage or wear. This includes inspecting the wiring, connections, and solar panels themselves. Look for any frayed wires, loose connections, or physical damage to the panels. Any faulty components should be replaced promptly to avoid disruption in energy production.
Checking and replacing faulty components in a solar panel system is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and prolonging the lifespan of the system. Here’s a guide on how to check for and replace faulty components:
-
Identify Symptoms of Faulty Components:
- Look for signs indicating potential issues with the solar panel system, such as reduced energy production, abnormal system behavior, error messages on inverters, or physical damage to components. These symptoms can help pinpoint the location and nature of the fault.
-
Perform Visual Inspection:
- Inspect the components of the solar panel system visually for any visible damage, wear and tear, loose connections, or signs of overheating. Check the solar panels, wiring, junction boxes, inverters, charge controllers, and batteries for physical abnormalities.
-
Check Electrical Connections:
- Verify the integrity of electrical connections, terminals, and wiring throughout the system. Tighten any loose connections, replace damaged cables or connectors, and ensure proper insulation to prevent electrical faults or short circuits.
-
Test Voltage and Current:
- Use a multimeter or clamp meter to measure the voltage and current output of the solar panels, inverters, and other components. Compare the measured values to the expected specifications provided by the manufacturer to identify any discrepancies or abnormalities.
-
Troubleshoot Inverter Issues:
- If the inverter is displaying error messages or malfunctioning, troubleshoot the inverter by checking input voltage, output voltage, and status indicators. Refer to the manufacturer’s manual for troubleshooting guidelines and error code explanations.
-
Inspect Battery Health:
- If the solar panel system includes batteries, monitor the health and performance of the batteries regularly. Check battery voltage, state of charge, electrolyte levels (for flooded lead-acid batteries), and overall condition to ensure proper operation.
-
Replace Faulty Components:
- Once you have identified the faulty components, replace them promptly with new or compatible replacements. Purchase replacement parts from reputable suppliers or contact the original manufacturer for genuine components and warranty support.
-
Follow Safety Guidelines:
- When replacing faulty components, follow appropriate safety precautions to prevent electrical hazards or personal injury. Turn off the system, wear insulated gloves and safety goggles, and work with caution around live electrical circuits.
-
Document Maintenance Activities:
- Keep detailed records of maintenance activities, including component replacements, repairs, and system performance evaluations. Documenting maintenance tasks can help track system history, identify recurring issues, and facilitate warranty claims if necessary.
-
Schedule Regular Inspections:
- Establish a regular inspection and maintenance schedule for the solar panel system to proactively identify and address potential issues before they escalate. Regular inspections can help prevent downtime, optimize system performance, and extend component lifespan.
Monitoring Energy Output
Keep a close eye on the energy output of your solar panels. Monitoring the performance can help you identify potential issues early on. Consider using a monitoring system that allows you to track the energy production on a daily basis. This will enable you to detect any irregularities and take action as needed to maintain consistent energy generation.
Addressing Power Interruptions
Power interruptions can be disruptive to a solar panel system, impacting energy production and potentially causing system downtime. Addressing these interruptions promptly is crucial to maintaining system efficiency. Here are steps to address power interruptions in a solar panel system:
-
Check for Grid Power Issues:
- Verify whether the power interruption is due to issues with the grid or utility supply. Check if neighboring properties are also experiencing power outages. If it is a grid-related issue, contact the utility company for updates and estimated restoration times.
-
Inspect System Components:
- Conduct a visual inspection of the solar panel system components, including the solar panels, wiring, inverters, and disconnect switches. Look for any visible damage, loose connections, or abnormal indicators on the inverters.
-
Monitor Inverter Status:
- Check the status and indicators on the inverters. Some inverters provide error codes or status messages that can help identify the cause of the interruption. Refer to the manufacturer’s manual or online resources for guidance on interpreting inverter status.
-
Reset Inverters and Disconnect Switches:
- If safe to do so, reset the inverters and disconnect switches. Power cycling these components may resolve minor issues or glitches. Follow proper safety procedures and ensure that all relevant safety precautions are taken before resetting.
-
Review Monitoring Data:
- If the solar panel system has a monitoring system in place, review the data to identify any patterns or anomalies leading up to the power interruption. Monitoring data can provide insights into the system’s performance and help diagnose potential issues.
-
Check for Overheating:
- Inspect the components for signs of overheating, especially during periods of extended power interruptions. Overheating can occur in the inverter or other electrical components and may require additional ventilation or cooling measures.
-
Contact Technical Support or Installer:
- If the cause of the power interruption is not apparent or cannot be resolved through basic troubleshooting, contact the technical support provided by the solar panel system manufacturer or installer. They can offer guidance, perform remote diagnostics, or schedule on-site assistance if necessary.
-
Consider Battery Backup Solutions:
- To mitigate the impact of power interruptions, consider integrating a battery backup solution into the solar panel system. Batteries can store excess energy generated during the day and provide power during periods of low or no sunlight, ensuring continuous operation even during grid outages.
-
Implement Redundancy Measures:
- Explore options for redundancy or backup power sources, such as backup generators or uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems. These measures can provide temporary power during extended outages, allowing critical loads to continue operating.
-
Update Emergency Response Plan:
- Maintain an emergency response plan that outlines procedures for addressing power interruptions and system issues. Ensure that relevant personnel are familiar with the plan and can execute the necessary steps to minimize downtime.
In the event of power interruptions, it’s important to be prepared to address the issue promptly. Whether it’s due to a technical fault or external factors, having a plan in place to restore power is crucial. Consider having a backup power source or a generator on hand to ensure continuous energy supply during interruptions.
By adhering to these maintenance and troubleshooting tips, you can keep your solar panel system running smoothly without the need for a battery, maximizing its efficiency and longevity.
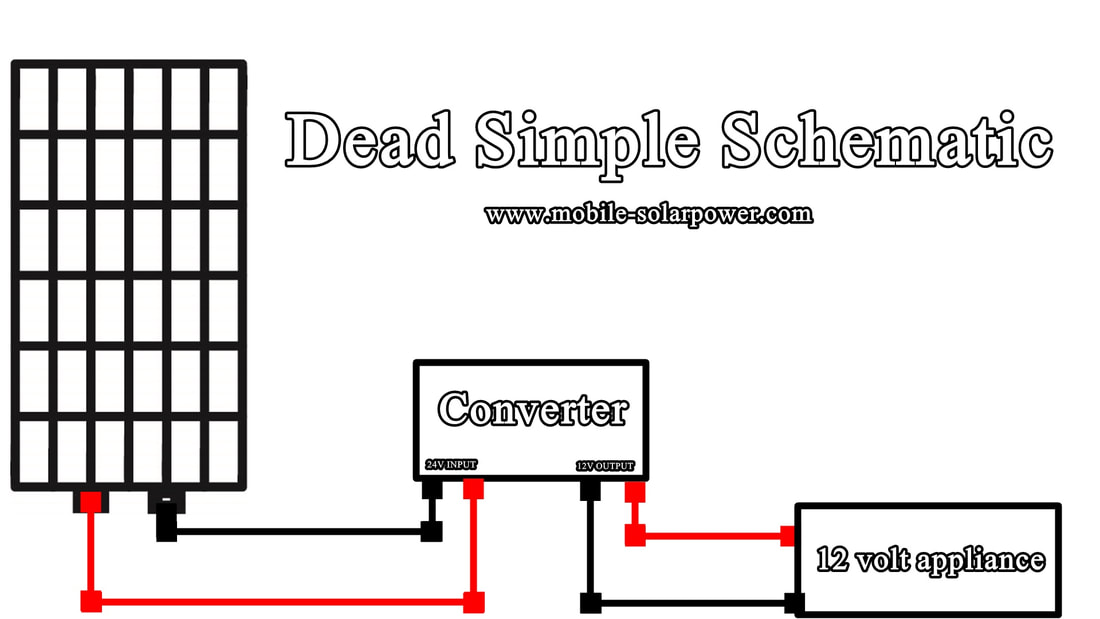
Credit: www.mobile-solarpower.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of How To Use Solar Panel Directly Without Battery
How Can I Use Solar Panels Without A Battery?
You can directly connect solar panels to your devices or appliances during daylight hours for immediate power consumption.
What Are The Advantages Of Using Solar Panels Directly Without A Battery?
By bypassing the need for a battery, you can save costs on purchasing and maintaining battery storage, and also increase efficiency in energy usage.
Can I Power My Home Using Solar Panels Without A Battery?
Yes, it’s possible to power your home using solar panels without a battery. However, you will only have electricity during daylight hours.
Conclusion
Using solar panels directly without a battery is a practical and economical option for harnessing renewable energy. By understanding the benefits and limitations of this approach, you can make an informed decision for your energy needs. With the right setup, you can enjoy the advantages of solar energy without the need for costly battery storage.