Solar panels can be used at home by installing them on the roof and connecting them to the electrical system. How to Use Solar Panels Harnessing the power of the sun, solar panels generate electricity that can be used to power various appliances and reduce reliance on the grid.

By utilizing solar energy, homeowners can save money on utility bills and contribute to a more sustainable environment. With the advancements in technology, solar panels have become more affordable and efficient, making them a viable option for many households. Additionally, there are various incentives and rebates available to encourage homeowners to switch to solar power.
Installing solar panels at home allows individuals to take control of their energy consumption and make a positive impact on the planet.

Credit: www.cnet.com
Benefits Of Using Solar Panels At Home
solar panels at home offers numerous benefits, both for homeowners and the environment. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Renewable Energy Source: Solar panels harness sunlight, a virtually limitless and renewable energy source. Unlike finite fossil fuels, sunlight is abundant and freely available, making solar energy a sustainable and environmentally friendly choice.
-
Reduced Electricity Bills: By generating your own electricity from solar panels, you can significantly reduce or even eliminate your reliance on grid-supplied electricity. This can lead to substantial savings on electricity bills over the long term, especially as energy prices continue to rise.
-
Energy Independence: Solar panels provide homeowners with greater energy independence and resilience. By generating your own electricity on-site, you become less vulnerable to power outages, utility disruptions, and fluctuating energy prices.
-
Low Operating Costs: Once installed, solar panels have minimal operating costs. They require little maintenance beyond occasional cleaning to ensure optimal performance. With no fuel costs or ongoing expenses, solar power offers predictable and stable energy costs over the system’s lifespan.
-
Financial Incentives and Rebates: Many governments offer financial incentives, tax credits, and rebates to encourage the adoption of solar energy. These incentives can help offset the initial cost of solar panel installation, making solar power more accessible and affordable for homeowners.
-
Increased Property Value: Solar panels can enhance the value of your home. Studies have shown that homes equipped with solar energy systems tend to sell faster and at higher prices than comparable properties without solar installations. Solar panels are seen as desirable features by homebuyers seeking energy-efficient homes and long-term savings.
-
Environmental Benefits: Solar energy is a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. By generating electricity from sunlight, solar panels produce no air or water pollution and have a minimal carbon footprint over their lifecycle.
-
Job Creation and Economic Growth: The solar industry creates jobs and stimulates economic growth. Solar panel manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and related services contribute to employment opportunities in local communities and support a growing green economy.
-
Grid Stabilization and Reliability: Distributed solar power generation can help stabilize the electricity grid by reducing strain during peak demand periods. By generating electricity closer to where it is consumed, solar energy can alleviate stress on transmission and distribution infrastructure, improving grid reliability and resilience.
-
Educational and Community Benefits: Solar panel installations can raise awareness about renewable energy and inspire community engagement. Homeowners who install solar panels often become advocates for clean energy and may share their experiences and knowledge with others, contributing to broader sustainability initiatives and environmental education efforts.
Solar panels offer numerous benefits to homeowners, ranging from lowering electricity bills to contributing to a cleaner environment. By harnessing the sun’s energy, you can enjoy greater energy independence and reduce your carbon footprint. Let’s explore these advantages in more detail:
Lower Electricity Bills
Installing solar panels at home can significantly lower your electricity bills. By generating your own renewable energy, you can reduce your reliance on traditional power sources, resulting in substantial cost savings over time.
Environmental Impact
Using solar panels has a positive environmental impact. It helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and decreases reliance on fossil fuels, thereby contributing to a healthier planet. Switching to solar energy also supports the global transition towards sustainable and renewable energy sources.
Energy Independence
By utilizing solar panels, homeowners can achieve energy independence. Generating your own electricity reduces reliance on external energy suppliers and allows you to have more control over your energy consumption and production. This enhances resiliency during power outages and enables you to contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Assessing Your Home’s Solar Potential
Assessing your home’s solar potential is an important step in determining whether solar panels are a viable option for your property. Here are some key factors to consider when evaluating your home’s solar potential:
-
Roof Orientation and Angle:
- Orientation: South-facing roofs typically receive the most sunlight in the northern hemisphere (north-facing in the southern hemisphere). However, east and west-facing roofs can also be suitable for solar installations, depending on your location and energy needs.
- Angle: The optimal tilt angle for solar panels is generally equal to your latitude, but adjustments may be made to maximize energy production based on your specific circumstances.
-
Available Roof Space:
- Determine the available roof space for solar panel installation. Consider factors such as roof size, shape, obstructions (such as chimneys, vents, or skylights), and shading from nearby trees or buildings that could impact solar access.
-
Sun Exposure:
- Assess the amount of sunlight your roof receives throughout the day and year. Factors such as shading from nearby structures or landscape features can affect sun exposure and solar potential. Tools like solar pathfinder or online solar mapping tools can help evaluate sun exposure.
-
Local Climate and Weather Patterns:
- Consider local climate conditions, weather patterns, and seasonal variations in sunlight exposure. Cloud cover, fog, and air pollution can affect solar panel performance and energy production.
-
Energy Consumption:
- Evaluate your household’s energy consumption patterns and electricity needs. Understanding your energy usage can help determine the size and capacity of the solar energy system needed to offset your electricity usage and achieve your energy goals.
-
Regulatory and Permitting Requirements:
- Research local zoning regulations, building codes, and permitting requirements related to solar panel installations. Some areas may have restrictions on solar installations or require permits for grid-tied systems.
-
Financial Considerations:
- Assess the financial aspects of going solar, including upfront costs, available incentives, tax credits, financing options, and potential return on investment (ROI). Calculate the payback period and long-term savings associated with solar panel installation.
-
Solar Resource Potential:
- Use online solar tools, such as the National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s PV Watts calculator or Google’s Project Sunroof, to estimate your home’s solar resource potential and energy production potential based on location-specific data.
-
Consultation with Solar Professionals:
- Consider consulting with solar energy professionals or reputable solar installers for a comprehensive evaluation of your home’s solar potential. They can provide site assessments, energy audits, and customized solar solutions tailored to your specific needs and circumstances.
If you’re considering integrating solar panels into your home’s energy infrastructure, it’s essential to first assess your home’s solar potential. By carefully evaluating factors such as sun exposure, roof space, and energy consumption, you can determine whether your home is a suitable candidate for solar panel installation. Let’s explore each of these considerations in detail:
Determining Sun Exposure
To maximize the benefits of solar energy, it’s crucial to evaluate your home’s sun exposure. Remember, solar panels require direct sunlight to generate electricity efficiently. Start by identifying the areas around your home that receive the most sunlight throughout the day. Typically, south-facing roofs tend to have the highest sun exposure, making them ideal for solar panel installation. Additionally, keep an eye out for any potential shade sources such as nearby trees, tall buildings, or structures that might obstruct sunlight and reduce the solar panel’s effectiveness.
Analyzing Roof Space
Once you’ve determined the sunniest areas of your property, it’s time to analyze your roof space. Evaluate whether your roof is in good condition and has enough space to accommodate solar panels. A well-maintained roof with adequate space will ensure proper installation and efficiency. Consider factors such as the roof’s angle, orientation, and structural integrity. A steep roof angle facing south will optimize solar panel efficiency, allowing them to capture the maximum amount of sunlight. It’s also essential to assess whether your roof can support the additional weight of the solar panels. In case your roof isn’t suitable or doesn’t offer sufficient space, ground-mounted solar panels could be an alternative worth exploring.
Evaluating Energy Consumption
Assessing your home’s energy consumption is crucial for determining the number of solar panels needed. Analyze your electricity bills from the past year to gain insights into your average consumption patterns. By understanding your energy needs, you can identify the size and capacity of the solar panel system required. Evaluating energy consumption also allows you to estimate potential cost savings on your electricity bills once solar panels are installed. It’s worth noting that energy-efficient practices and appliances can further reduce your electricity consumption, enabling you to optimize the benefits of solar energy.
Choosing The Right Solar Panels
the right solar panels for your home or project involves considering several important factors to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability. Here are key factors to consider when selecting solar panels:
-
Solar Panel Types:
- Monocrystalline: Made from single-crystal silicon, monocrystalline solar panels offer high efficiency and performance, making them ideal for limited roof space or areas with high electricity costs.
- Polycrystalline: Constructed from multiple silicon crystals, polycrystalline solar panels are cost-effective and suitable for larger installations with ample roof space.
- Thin-Film: Thin-film solar panels are lightweight and flexible, making them suitable for non-traditional installations or applications where aesthetics and versatility are important.
-
Efficiency:
- Consider the efficiency rating of solar panels, which indicates the amount of sunlight converted into electricity. Higher efficiency panels typically produce more power per square foot and are ideal for installations with limited space.
-
Durability and Longevity:
- Look for solar panels with durable construction and robust materials designed to withstand harsh weather conditions, including wind, rain, snow, and hail. Consider the warranty offered by the manufacturer, including performance guarantees and product warranties.
-
Brand Reputation and Reliability:
- Choose reputable solar panel manufacturers with a proven track record of quality, reliability, and longevity. Research customer reviews, industry certifications, and third-party testing results to assess the reputation of the brand.
-
Aesthetic Considerations:
- Consider the appearance and design of solar panels, especially if aesthetics are important for your installation. Some panels offer sleek, black frames or integrated mounting systems for a more streamlined look.
-
Cost and Value:
- Evaluate the upfront cost of solar panels and consider the long-term value they provide in terms of energy savings, return on investment (ROI), and environmental benefits. Compare the cost per watt and total cost of ownership when assessing different panel options.
-
Size and Power Output:
- Determine the size and power output of solar panels based on your energy needs and available roof space. Calculate the total wattage required to offset your electricity usage and select panels that can meet or exceed your energy requirements.
-
Temperature Coefficient:
- Consider the temperature coefficient of solar panels, which indicates how their performance degrades at higher temperatures. Choose panels with lower temperature coefficients for improved performance in hot climates.
-
Compatibility with Mounting Systems:
- Ensure that the solar panels are compatible with your chosen mounting system, whether roof-mounted, ground-mounted, or integrated into building materials. Consider factors such as tilt angle, orientation, and shading when designing the mounting configuration.
-
Incentives and Rebates:
- Check for available incentives, rebates, tax credits, and financing options offered by government agencies, utility companies, or solar installers. These incentives can help offset the upfront cost of solar panel installation and increase the overall value proposition.
Choosing the right solar panels is a crucial step in harnessing solar energy for your home. With various options available in the market, it’s important to understand the different types of solar panels, their efficiency and performance, as well as their warranty and durability. To help you make an informed decision, let’s take a closer look at each of these factors.
Types Of Solar Panels
There are three main types of solar panels commonly used in residential settings:
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels: These panels are made from a single crystal structure, making them highly efficient and able to generate more electricity in limited space.
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels: Polycrystalline panels are made up of multiple crystals, which makes them less efficient than monocrystalline panels, but also more affordable.
- Thin-Film Solar Panels: These panels are made by depositing a thin layer of photovoltaic material onto a substrate. They are flexible and lightweight, making them suitable for certain applications where traditional solar panels may not be viable.
Efficiency And Performance
The efficiency of solar panels refers to how much sunlight they can convert into electricity. Higher efficiency panels typically generate more electricity and require less space, which can be advantageous if you have limited roof space. However, it’s important to balance efficiency with cost-effectiveness, as higher efficiency panels often come with a higher price tag. Consider your energy needs and available space to determine the optimal efficiency for your home.
Warranty And Durability
When investing in solar panels, it’s essential to consider their warranty and durability. A longer warranty period indicates the manufacturer’s confidence in the product’s quality and performance. Look for solar panels with warranties of at least 25 years, as they provide long-term security and peace of mind. Additionally, consider the durability of the panels, especially if you live in an area prone to extreme weather conditions. High-quality panels should be able to withstand harsh weather elements and have a sturdy construction that ensures longevity.
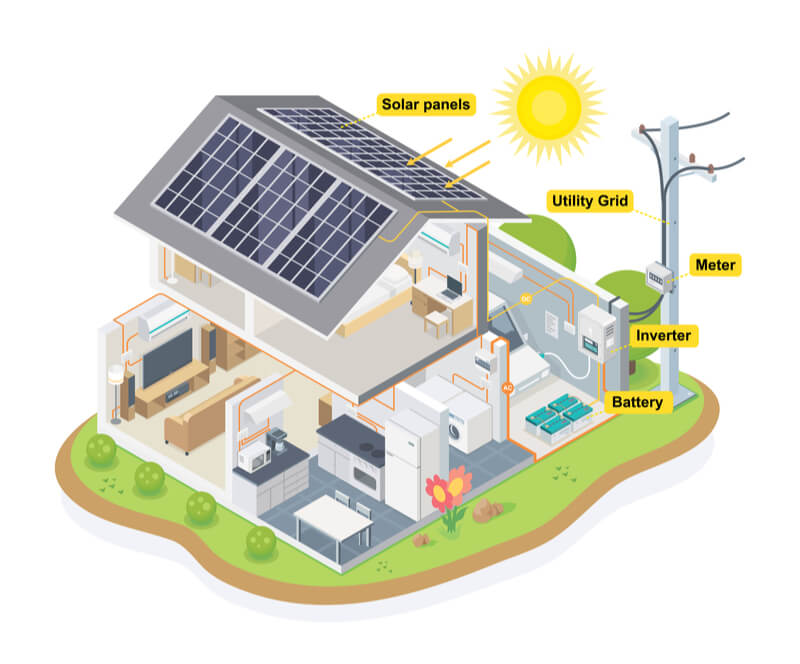
Credit: www.saveonenergy.com
Calculating Your Solar Panel Needs
Calculating your solar panel needs involves several steps to determine the size and capacity of the solar energy system required to meet your electricity needs. Here’s a guide to help you calculate your solar panel needs:
-
Determine Your Average Daily Energy Consumption:
- Review your electricity bills from the past 12 months to determine your average daily energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Divide the total annual kWh usage by 365 days to obtain the average daily usage.
-
Assess Your Roof’s Solar Potential:
- Evaluate your roof’s solar potential by considering factors such as orientation, tilt angle, shading, and available roof space. South-facing roofs with minimal shading typically receive the most sunlight and are ideal for solar installations.
-
Calculate Solar Panel Capacity Needed:
- Determine the capacity of solar panels needed to generate enough electricity to meet your daily energy consumption. Divide your average daily energy usage (in kWh) by the average daily sunlight hours in your area to calculate the required solar panel capacity in kilowatts (kW).
Example Calculation: Average Daily Energy Consumption = 30 kWh Average Daily Sunlight Hours = 5 hours Solar Panel Capacity Needed = 30 kWh / 5 hours = 6 kW
-
Consider System Efficiency and Losses:
- Account for system inefficiencies and losses when calculating solar panel needs. Factors such as shading, panel orientation, temperature, and inverter efficiency can affect overall system performance. Apply a derating factor (typically 0.75 to 0.85) to adjust for these losses.
Example Adjustment: Solar Panel Capacity Needed (after derating) = 6 kW / 0.85 = 7.06 kW
-
Select Solar Panel Size and Quantity:
- Choose solar panels with appropriate size and wattage ratings based on your calculated capacity needs. Consider factors such as panel efficiency, physical dimensions, and available roof space when selecting panel size and quantity.
Example: If you choose 400W solar panels, you would need approximately 18 panels to achieve a total capacity of 7.06 kW (7,060 watts / 400 watts per panel = 17.65 panels).
-
Assess Financial Considerations:
- Evaluate the cost of the solar energy system, including solar panels, inverters, mounting hardware, and installation. Consider available incentives, rebates, tax credits, and financing options to offset upfront costs and maximize savings.
-
Consult with Solar Professionals:
- Consider consulting with solar professionals or reputable installers for a comprehensive assessment of your solar panel needs. They can provide site evaluations, energy audits, and customized solar solutions tailored to your specific requirements and budget.
When it comes to using solar panels at home, calculating your solar panel needs is crucial for an effective and efficient setup. Estimating your energy requirements, considering off-grid systems, and determining the sizing and array configuration are essential steps in this process. Let’s dive into these aspects and learn how to calculate your solar panel needs to harness the power of the sun.
Estimating Energy Requirements
Before installing solar panels, it’s important to know your energy needs. Estimate the average daily energy consumption of your household in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Consider appliances, lighting, electronics, and heating and cooling systems. This data will help in determining the number of solar panels required to meet your energy demands.
Considerations For Off-grid Systems
For those opting for an off-grid solar system, special considerations come into play. Assess the average daily energy consumption, available sunlight hours, and energy storage capacity needed for days with low sunlight. Off-grid systems require batteries to store excess energy for use during periods of low solar power generation.
Sizing And Array Configuration
When it comes to sizing your solar panel system, calculate the total wattage needed based on your energy requirements. Consider factors such as sunlight hours, panel efficiency, and geographic location to determine the number and size of solar panels. The array configuration, including tilt and orientation, also impacts the system’s performance and should be optimized for maximum sunlight exposure.
Installing Solar Panels
Installing solar panels involves several steps to ensure a safe, efficient, and reliable solar energy system. Here’s a general overview of the solar panel installation process:
-
Site Assessment and Planning:
- Conduct a site assessment to evaluate the suitability of your property for solar panel installation. Consider factors such as roof orientation, tilt angle, shading, structural integrity, and local regulations. Determine the optimal location and configuration for solar panels to maximize sunlight exposure and energy production.
-
Designing the Solar Energy System:
- Work with a solar professional or installer to design a customized solar energy system based on your energy needs, roof characteristics, and budget. The design process includes selecting the appropriate solar panel size and quantity, inverter type, mounting system, and electrical components.
-
Obtaining Permits and Approvals:
- Obtain necessary permits and approvals from local authorities, homeowners’ associations, or utility companies before proceeding with the installation. Ensure compliance with building codes, zoning regulations, and safety standards applicable to solar panel installations in your area.
-
Procuring Solar Panels and Equipment:
- Purchase high-quality solar panels, inverters, mounting hardware, and electrical components from reputable manufacturers or suppliers. Consider factors such as panel efficiency, warranty coverage, and compatibility with your solar energy system.
-
Preparation and Roof Work:
- Prepare the installation site by cleaning the roof surface and making any necessary repairs or reinforcements to ensure structural integrity. Install roof flashing, racking systems, and mounting hardware according to manufacturer specifications.
-
Installing Solar Panels:
- Position and secure the solar panels onto the mounting rails or frames using appropriate fasteners and hardware. Follow the layout and orientation determined during the design phase to optimize sunlight exposure and minimize shading. Connect the panels in series or parallel to form strings and arrays.
-
Electrical Wiring and Connections:
- Install electrical wiring, conduits, junction boxes, and disconnect switches to connect the solar panels, inverters, and other system components. Follow electrical codes and safety standards to ensure proper wiring, grounding, and protection against electrical hazards.
-
Inverter Installation:
- Mount and wire the inverters according to manufacturer guidelines. Choose the appropriate type of inverter (string inverters, microinverters, or power optimizers) based on system design and requirements. Test the inverters to ensure they are functioning correctly.
-
Grid Connection and Interconnection:
- Connect the solar energy system to the electrical grid by installing a grid-tied inverter and interconnection equipment. Coordinate with your utility company to arrange for grid connection, metering, and net metering agreements if applicable.
-
Commissioning and Testing:
- Conduct system commissioning and testing to verify proper installation, functionality, and performance. Perform electrical tests, insulation resistance tests, voltage checks, and system startup procedures to ensure everything is working as intended.
-
Final Inspection and Certification:
- Schedule a final inspection with local authorities or utility representatives to verify compliance with regulations and safety standards. Obtain necessary certifications and approvals to operate the solar energy system legally and qualify for incentives or rebates.
-
Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Implement a monitoring and maintenance plan to track system performance, detect potential issues, and ensure optimal operation over time. Regularly inspect the solar panels, inverters, wiring, and connections for signs of damage, wear, or malfunction.
Installing solar panels is an effective way to harness the power of the sun and reduce your carbon footprint. Whether you choose to hire a professional or go the DIY route, obtaining permits and approvals, as well as properly positioning and mounting your panels, are essential steps to ensure a successful solar panel installation. In this article, we will explore each of these steps in detail to help you navigate the process seamlessly.
Hiring A Professional Or DIY
If you are considering installing solar panels, one of the first decisions you’ll need to make is whether to hire a professional installer or take a DIY approach. Each option has its pros and cons, so it’s essential to evaluate your skills, the complexity of your installation, and your budget.
When it comes to hiring a professional, there are several benefits to consider. Experienced installers have the knowledge and expertise to handle all aspects of the installation, from obtaining permits to wiring the panels correctly. Additionally, they can provide warranties and guarantees for their work, giving you peace of mind.
On the other hand, if you have a good understanding of electrical systems and enjoy a good DIY project, installing solar panels yourself can be a rewarding experience. It allows you to have full control over the installation process and potentially save on labor costs. However, keep in mind that solar panel installation requires technical know-how, and any mistakes can negatively affect the performance and safety of your system. So, make sure you thoroughly research and educate yourself before embarking on a DIY installation.
Obtaining Permits And Approvals
Before you begin the installation process, it’s crucial to obtain the necessary permits and approvals to ensure compliance with local regulations. Permitting requirements can vary depending on your location, so it’s essential to contact your local building department or a solar professional to understand the specific guidelines you need to follow.
Typically, you’ll need to submit detailed plans and specifications, including information on your intended solar panel layout, electrical connections, and structural considerations. Additionally, you may need to provide engineering reports and certifications to ensure the safety and stability of your installation. These steps are in place to protect both you and your property, as well as to ensure that your solar panel system meets all safety and quality standards.
Positioning And Mounting
Proper positioning and mounting of solar panels are vital for optimal energy production. The primary goal is to maximize sun exposure throughout the day. To achieve this, your panels should be orientated at the ideal tilt and azimuth angle, facing the sun’s path.
When positioning your panels, consider any potential obstructions such as trees, buildings, or shading from nearby structures. Obstructions can significantly impact the performance of your system and reduce solar energy production. It’s crucial to choose a location that receives abundant sunlight, preferably in an unobstructed area, such as the roof of your house or a large open space on your property.
Once you’ve determined the ideal location, proper mounting becomes essential. Solar panels can be mounted on different types of surfaces, such as roofs, poles, or even on the ground. Selecting the appropriate mounting system and ensuring secure installation is crucial to prevent any damage, especially during extreme weather conditions. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and consult a professional if you’re unsure about the best mounting solution for your specific circumstances.
Maintaining And Monitoring Solar Panels
Maintaining and monitoring solar panels is essential to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity of your solar energy system. Here are some key maintenance and monitoring practices to keep your solar panels operating at their best:
-
Regular Cleaning:
- Keep solar panels clean and free of debris, dust, dirt, pollen, bird droppings, and other obstructions that may accumulate on the surface. Clean panels using water, a soft brush, and a mild detergent if needed. Avoid abrasive materials or harsh chemicals that could scratch or damage the panels.
-
Inspecting for Damage:
- Conduct periodic visual inspections of the solar panels, mounting hardware, wiring, and connections to check for signs of damage, wear, corrosion, or degradation. Look for cracks, chips, hotspots, discoloration, loose fasteners, or physical damage caused by weather, wildlife, or debris.
-
Monitoring Performance:
- Use monitoring software or online platforms provided by your solar installer or manufacturer to track and analyze system performance metrics, including energy production, power output, voltage, current, and environmental conditions. Monitor for any deviations or anomalies that may indicate underlying issues or inefficiencies.
-
Checking Inverters and Electronics:
- Monitor the performance of inverters, charge controllers, and other electronic components to ensure they are operating within normal parameters. Check for error codes, fault messages, or performance fluctuations that may require troubleshooting or maintenance.
-
Testing Electrical Connections:
- Periodically test electrical connections, junction boxes, wiring, and grounding systems to ensure they are secure, tight, and free of corrosion or degradation. Perform insulation resistance tests and voltage checks to verify electrical integrity and safety.
-
Inspecting Roof and Mounting Hardware:
- Inspect the roof surface, flashing, racking systems, and mounting hardware to ensure they are secure, stable, and free of damage. Check for signs of leaks, water intrusion, or structural issues that may affect the integrity of the solar panel installation.
-
Shade Management:
- Monitor for changes in shading patterns caused by vegetation growth, nearby buildings, or other obstructions that may impact solar panel performance. Trim trees, bushes, or foliage as needed to minimize shading and maximize sunlight exposure.
-
Seasonal Adjustments:
- Make seasonal adjustments to tilt angles or orientation of solar panels to optimize energy production during different times of the year. Adjust panel angles to capture more sunlight in winter months and reduce overheating in summer months.
-
Addressing Performance Issues Promptly:
- Take immediate action to address any performance issues, faults, or alarms detected during monitoring. Troubleshoot the root cause of the problem and consult with solar professionals or technicians for repairs, replacements, or adjustments as needed.
-
Documenting Maintenance Activities:
- Keep detailed records of maintenance activities, inspections, repairs, and performance data over time. Maintain documentation of warranties, service contracts, and communication with installers or manufacturers for reference and warranty claims.
If you’ve made the wise decision to switch to solar power, congratulations! By harnessing the sun’s energy, you’ll enjoy a sustainable and renewable source of electricity for your home. However, it’s important to remember that solar panels require regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure optimal performance and longevity. In this section, we’ll guide you on how to effectively care for and monitor your solar panels so they can continue to operate efficiently for years to come.
Cleaning And Inspecting
Regular cleaning and inspection are crucial for keeping your solar panels in top shape. Dust, dirt, pollen, leaves, and bird droppings can accumulate on the surface of your panels and reduce their efficiency. To clean your panels, follow these steps:
- First, check the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure there are no specific cleaning requirements.
- Make sure your panels are cool to the touch before cleaning to avoid thermal shock.
- Spray the panels with a garden hose to remove loose debris.
- Use a soft sponge or cloth soaked in warm, soapy water to gently scrub the surface.
- Rinse the panels thoroughly with clean water and allow them to air dry.
In addition to cleaning, you should also inspect your panels regularly. Look for any signs of damage, such as cracks, loose connections, or exposed wiring. If you notice any issues, contact a professional solar technician for assistance.
Checking Performance
To ensure that your solar panels are operating at their maximum efficiency, it’s important to monitor their performance. Here are some steps you can take:
- Check your solar inverter’s display to see if it’s producing electricity. The inverter converts the DC electricity generated by your panels into usable AC electricity.
- Monitor your electricity bill to compare it with previous months. A significant increase may indicate a drop in your solar panel performance.
- If your solar system is equipped with monitoring software, utilize it to track your system’s performance, daily energy production, and any potential issues.
- Keep an eye out for shaded areas on your panels, as they can impact performance. Trim any overhanging trees or objects that may cast shadows.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Sometimes, despite your best efforts, issues may arise with your solar panels. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips to help you address them:
| Issue | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|
| Low energy production | Check for shading, dirt, or debris on the panels. Ensure proper alignment and tilt. Examine the inverter for any faults. |
| Inverter not working | Check the inverter’s display for error codes. Ensure it is receiving power. If the issue persists, contact a professional for assistance. |
| Intermittent power output | Inspect the wiring connections for any loose or damaged wires. Clean any corroded connectors and tighten them securely. |
| Frequent tripping of circuit breakers | Check for overloading or short circuits. Make sure the circuit breaker is properly rated for your solar system’s capacity. |
By proactively cleaning, inspecting, and monitoring your solar panels, you can ensure their optimal performance and maximize your energy savings in the long run.
Troubleshooting common issues with solar panels and solar energy systems is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and addressing potential problems promptly. Here are some common issues you may encounter and steps to troubleshoot them:
-
Reduced Energy Production:
- Possible Causes: Shading from trees, buildings, or obstructions; soiling or debris on panels; faulty panels or components; electrical issues; system inefficiencies.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check for shading during peak sunlight hours and trim vegetation if necessary.
- Clean the solar panels to remove dirt, dust, or debris using water and a soft brush.
- Inspect panels for damage, cracks, or defects that may affect performance.
- Monitor system performance metrics to identify any anomalies or deviations.
- Test electrical connections, inverters, and wiring for faults or malfunctions.
-
Inverter Faults or Error Codes:
- Possible Causes: Overheating, overvoltage, under voltage, overcurrent, ground fault, communication errors, software issues.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check the inverter display for error codes or fault messages and refer to the manufacturer’s manual for troubleshooting guidance.
- Reset the inverter and perform a reboot if necessary.
- Inspect the inverter for signs of damage, overheating, or loose connections.
- Verify that the DC and AC electrical connections are secure and properly grounded.
- Test the voltage, current, and output of the inverter using a multimeter or diagnostic tools.
-
Poor System Performance in Low Light Conditions:
- Possible Causes: Inefficient panels or system design; shading from clouds or weather conditions; dirty or soiled panels.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Clean the solar panels to remove dirt, dust, or debris that may reduce sunlight absorption.
- Check for shading caused by clouds, haze, or weather patterns and adjust expectations accordingly.
- Verify that the system design and configuration are optimized for low light conditions, such as using bypass diodes in shaded areas.
-
Intermittent Power Output or Fluctuations:
- Possible Causes: Loose connections, wiring faults, electrical shorts, intermittent shading, inverter issues, temperature variations.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect electrical connections, junction boxes, and wiring for loose or damaged components.
- Test the continuity and integrity of electrical circuits using a multimeter or diagnostic tools.
- Monitor environmental conditions and temperature fluctuations that may affect system performance.
- Check for intermittent shading from moving objects or temporary obstructions and adjust system configuration if necessary.
-
Metering and Monitoring Issues:
- Possible Causes: Meter calibration errors, communication failures, sensor malfunctions, software glitches.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Verify that meters, sensors, and monitoring equipment are properly installed and calibrated according to manufacturer specifications.
- Check for communication errors or signal interruptions between monitoring devices and the central monitoring system.
- Reset or reboot monitoring software or devices to resolve software glitches or connectivity issues.
- Consult with monitoring system providers or technical support for assistance with troubleshooting and diagnostics.
-
Storm or Weather Damage:
- Possible Causes: High winds, hail, lightning strikes, extreme temperatures, flooding, physical damage.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect solar panels, mounting hardware, and electrical components for signs of damage or wear caused by severe weather events.
- Assess the extent of damage and prioritize repairs or replacements as needed to restore system functionality.
- Take preventive measures to reinforce roof structures, secure mounting systems, and protect against future weather-related risks.
-
Grid Connection or Net Metering Issues:
- Possible Causes: Utility outages, metering errors, billing discrepancies, grid-tied inverter faults, utility company issues.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check for utility outages or disruptions in grid power supply that may affect grid connection or net metering arrangements.
- Verify that the grid-tied inverter is functioning properly and communicating with the utility grid as intended.
- Review utility bills and meter readings for accuracy and address any discrepancies with the utility company.
-
Battery Storage System Problems (If Applicable):
- Possible Causes: Battery degradation, charging or discharging issues, temperature fluctuations, software errors.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- Monitor battery performance and health indicators to identify signs of degradation or malfunction.
- Check battery connections, terminals, and wiring for corrosion, loose connections, or damage.
- Review battery charging and discharging settings, including voltage thresholds and charge controller configurations.
- Consult with battery manufacturers or technical support for guidance on troubleshooting and maintenance.
Maximizing Solar Panel Efficiency
Maximizing solar panel efficiency is crucial for optimizing energy production and maximizing the return on your investment in solar energy. Here are some strategies to help you enhance the efficiency of your solar panels:
-
Optimal Placement and Orientation:
- Ensure that solar panels are installed in a location with maximum sunlight exposure throughout the day. Orient panels towards the south (in the northern hemisphere) or north (in the southern hemisphere) to capture the most sunlight. Adjust panel tilt angle to match your latitude for optimal performance.
-
Minimize Shading:
- Avoid shading from nearby trees, buildings, or obstructions that can reduce solar panel efficiency. Trim vegetation, relocate structures, or install shading analysis tools to identify and mitigate shading issues.
-
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance:
- Keep solar panels clean and free of dirt, dust, debris, and bird droppings that can block sunlight and reduce efficiency. Clean panels with water and a soft brush periodically, especially in areas with high levels of pollution or airborne particles.
-
Temperature Management:
- Monitor and manage solar panel temperatures to prevent overheating, which can decrease efficiency. Ensure proper ventilation and airflow around panels to dissipate heat. Consider installing tilt mounts or shade structures to reduce solar panel temperatures in hot climates.
-
Use High-Efficiency Panels:
- Choose high-efficiency solar panels with advanced technology and superior performance characteristics. Monocrystalline panels typically offer higher efficiency compared to polycrystalline panels and are ideal for installations with limited space or high electricity costs.
-
Optimized Inverter Selection:
- Select inverters with high efficiency ratings and advanced features to maximize energy conversion and system performance. Consider using microinverters or power optimizers to mitigate shading effects and improve overall system efficiency.
-
MPPT Charge Controllers (For Off-Grid Systems):
- Install Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) charge controllers for off-grid solar systems to optimize energy harvesting from solar panels. MPPT controllers adjust the operating voltage and current to maximize power output under varying environmental conditions.
-
Energy Storage Systems (If Applicable):
- Integrate energy storage systems, such as batteries, to store excess solar energy generated during peak production periods for use during periods of low sunlight or high electricity demand. Battery storage can enhance system efficiency and increase self-consumption of solar power.
-
Monitoring and Performance Analysis:
- Implement monitoring systems and software to track system performance metrics, including energy production, power output, voltage, current, and environmental conditions. Analyze performance data regularly to identify trends, anomalies, or areas for improvement.
-
Regular Inspections and Tune-Ups:
- Conduct routine inspections and tune-ups of your solar energy system to ensure all components are functioning optimally. Inspect electrical connections, inverters, wiring, and mounting hardware for signs of damage, wear, or corrosion. Address any issues promptly to maintain peak efficiency.
Solar panels are a sustainable and efficient way to power your home while reducing your carbon footprint. Maximizing solar panel efficiency is key to getting the most out of this renewable energy source. By optimizing sun exposure, minimizing shading, and using energy-efficient appliances, you can make the most of your solar panels and cut down on traditional energy consumption.
Optimizing Sun Exposure
To optimize sun exposure, place your solar panels in a location where they can receive maximum sunlight, typically facing south and tilted at an angle matching your latitude. Removing any obstructions such as trees or buildings that may cast shadows on the panels will also help improve exposure.
Minimizing Shading
Minimizing shading is crucial for maximizing the efficiency of your solar panels. Trim any overhanging branches or nearby vegetation that may cast shadows on the panels, especially during peak sunlight hours. Positioning panels in areas with minimal shading throughout the day will ensure they can capture as much sunlight as possible.
Using Energy-efficient Appliances
Using energy-efficient appliances in your home can help maximize the benefits of your solar panels. Energy-efficient appliances consume less power, allowing you to make the most of the energy generated by your solar panels. This reduces the need to draw from the grid and maximizes your overall energy savings.
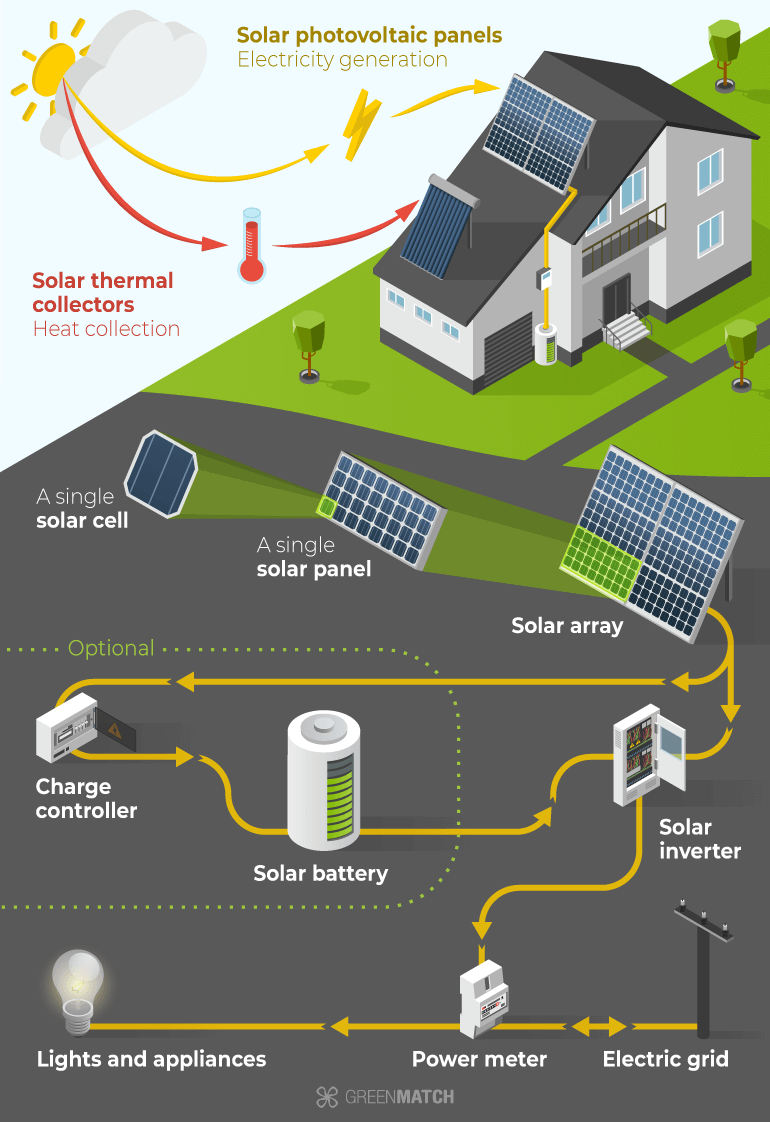
Credit: www.greenmatch.co.uk
Frequently Asked Questions For How To Use Solar Panels At Home
Can Solar Panels Be Used At Home?
Yes, solar panels can be used at home to generate clean and renewable energy for your household needs.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells, which capture the sun’s energy and convert it into usable electricity.
What Are The Benefits Of Using Solar Panels At Home?
Using solar panels at home can help you save money on electricity bills, reduce your carbon footprint, and increase the value of your property.
Conclusion
Incorporating solar panels is a sustainable choice for reducing energy costs and minimizing environmental impact. By harnessing solar energy, homeowners can contribute to a greener future while enjoying long-term savings. Embracing solar power at home empowers individuals to play a role in the global movement towards renewable energy.